Abstract
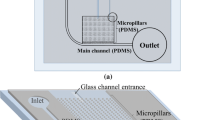
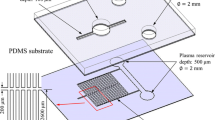
Since plasma is rich in many biomarkers used in clinical diagnostic experiments, microscale blood plasma separation is a primitive step in most of microfluidic analytical chips. In this paper, a passive microfluidic device for on-chip blood plasma separation based on Zweifach–Fung effect and plasma skimming was designed and fabricated by hot embossing of microchannels on a PMMA substrate and thermal bonding process. Human blood was diluted in various times and injected into the device. The main novelty of the proposed microfluidic device is the design of diffuser-shaped daughter channels. Our results demonstrated that this design exerted a considerable positive influence on the separation efficiency of the passive separator device, and the separation efficiency of 66.6 % was achieved. The optimum purity efficiency of 70 % was achieved for 1:100 dilution times.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhagat AAS et al (2010) Microfluidics for cell separation. Med Biol Eng Compu 48(10):999–1014
Chen X et al (2008) Microfluidic chip for blood cell separation and collection based on crossflow filtration. Sens Actuators B Chem 130(1):216–221
Cho YI, Back LH, Crawford DW (1985) Experimental investigation of branch flow ratio, angle, and Reynolds number effects on the pressure and flow fields in arterial branch models. J Biomech Eng 107(3):257–267
Choi S, Park J-K (2007) Continuous hydrophoretic separation and sizing of microparticles using slanted obstacles in a microchannel. Lab Chip 7(7):890–897
Doyeux V et al (2011) Spheres in the vicinity of a bifurcation: elucidating the Zweifach–Fung effect. J Fluid Mech 674:359–388
Fekete Z et al (2012) Performance characterization of micromachined particle separation system based on Zweifach–Fung effect. Sens Actuators B Chem 162(1):89–94
Fung Y-C (1973) Stochastic flow in capillary blood vessels. Microvasc Res 5(1):34–48
Geng Z et al (2011) A plasma separation device based on centrifugal effect and Zweifach–Fung effect. In: The 15th international conference on miniaturized systems for chemistry and life sciences
Hou HW et al (2011) Microfluidic devices for blood fractionation. Micromachines 2(3):319–343
Kanji S et al (2005) Reliability of point-of-care testing for glucose measurement in critically ill adults*. Crit Care Med 33(12):2778–2785
Kersaudy-Kerhoas M, Sollier E (2013) Micro-scale blood plasma separation: from acoustophoresis to egg-beaters. Lab Chip 13(17):3323–3346
Khumpuang S et al (2007) Blood plasma separation device using capillary phenomenon. In: Solid-state sensors, actuators and microsystems conference, 2007. TRANSDUCERS 2007. International: IEEE, 1967–1970
Kersaudy-Kerhoas M, Dhariwal R, Desmulliez MPY (2008) Recent advances in microparticle continuous separation. IET Nanobiotechnol 2(1):1–13
Kersaudy-Kerhoas MW et al (2010a) Validation of a blood plasma separation system by biomarker detection. Lab Chip 10(12):1587–1595
Kersaudy-Kerhoas MW et al (2010b) Hydrodynamic blood plasma separation in microfluidic channels. Microfluidics Nanofluidics 8(1):105–114
Kitaoka H, Takaki R, Suki BI (1999) A three-dimensional model of the human airway tree. J Appl Physiol 87(6):2207–2217
Leverett LB et al (1972) Red blood cell damage by shear stress. Biophys J 12(3):257
Li C et al (2012) The dual role of deposited microbead plug (DMBP): a blood filter and a conjugate reagent carrier toward point-of-care microfluidic immunoassay. Talanta 97:376–381
Sakamoto H et al (2012) Plasma separation PMMA device driven by capillary force controlling surface wettability. Micro Nano Lett IET 7(1):64–67
Shamsi A et al (2014) Low cost method for hot embossing of microstructures on PMMA by SU-8 masters. Microsyst Technol 20(10):1925–1931
Sollier E et al (2009) Passive microfluidic devices for plasma extraction from whole human blood. Sens Actuators B Chem 141(2):617–624
Sollier E et al (2010) Fast and continuous plasma extraction from whole human blood based on expanding cell-free layer devices. Biomed Microdevices 12(3):485–497
Svanes K, Zweifach BW (1968) Variations in small blood vessel hematocrits produced in hypothermic rats by micro-occlusion. Microvasc Res 1(2):210–220
Yamada M, Nakashima M, Seki M (2004) Pinched flow fractionation: continuous size separation of particles utilizing a laminar flow profile in a pinched microchannel. Anal Chem 76(18):5465–5471
Yang S, Ündar A, Zahn JD (2006) A microfluidic device for continuous, real time blood plasma separation. Lab Chip 6(7):871–880
Yoon JS, Germaine JT, Culligan PJ (2006) Visualization of particle behavior within a porous medium: Mechanisms for particle filtration and retardation during downward transport. Water Resour Res 42(6):W06417
Zhu Q, Trau D (2012) Multiplex detection platform for tumor markers and glucose in serum based on a microfluidic microparticle array. Anal Chim Acta 751:146–154
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. Shamsi and A. Shamloo contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shamsi, A., Shamloo, A., Mohammadaliha, N. et al. High throughput blood plasma separation using a passive PMMA microfluidic device. Microsyst Technol 22, 2447–2454 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2664-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2664-7